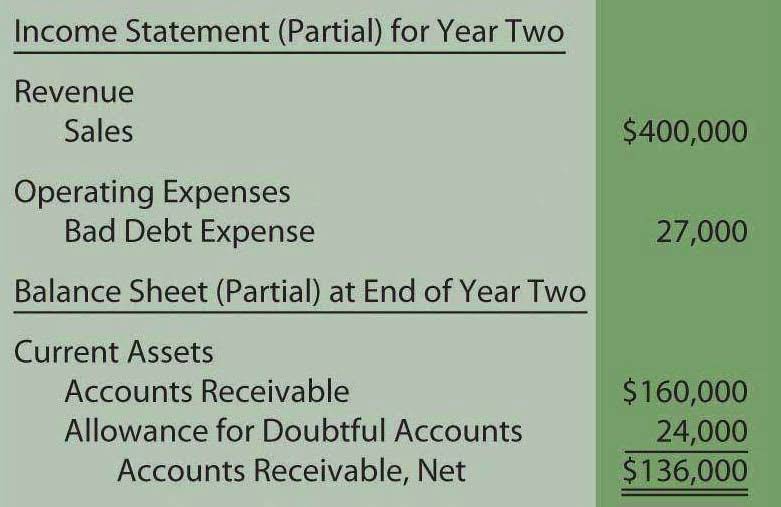
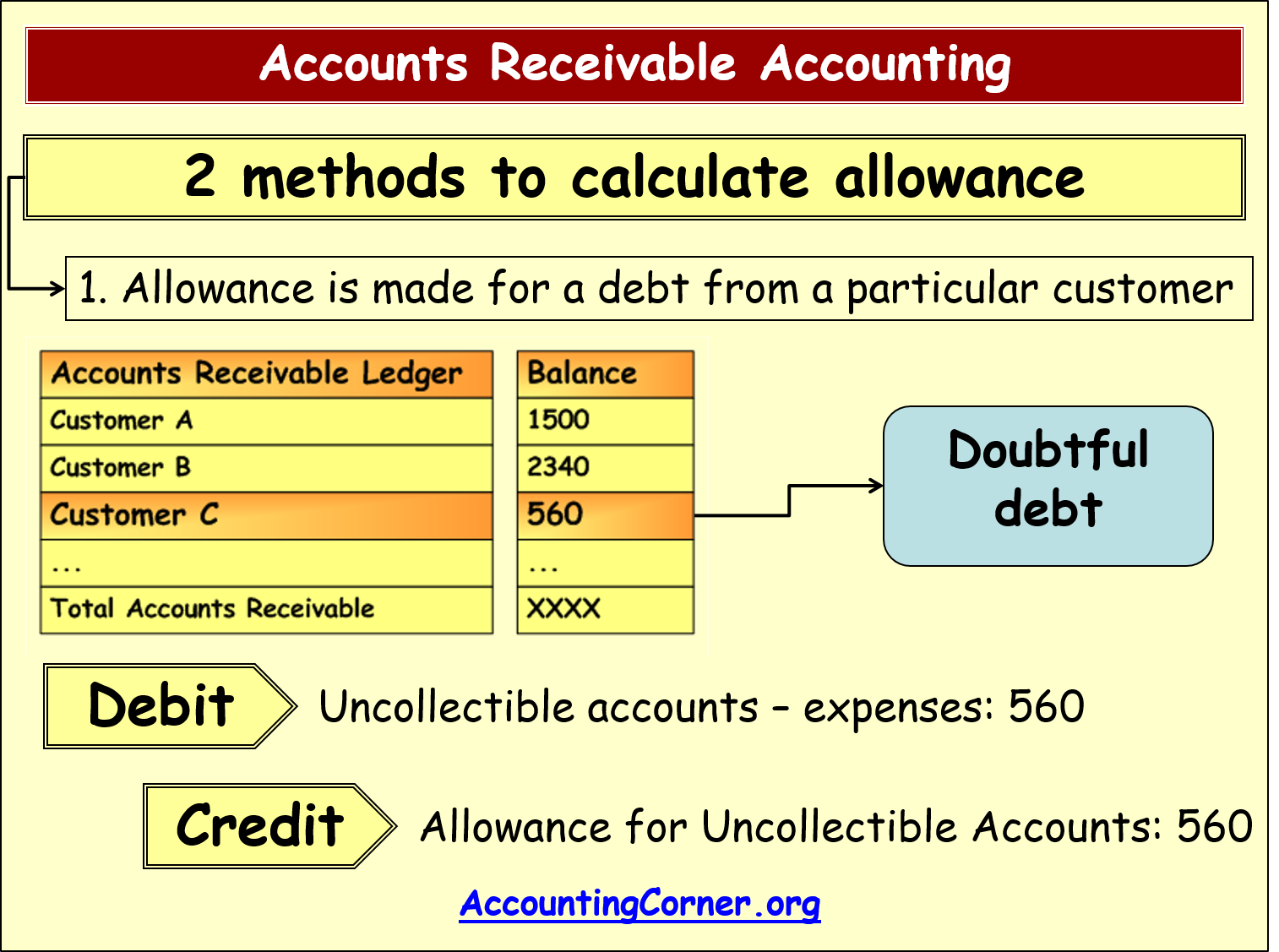
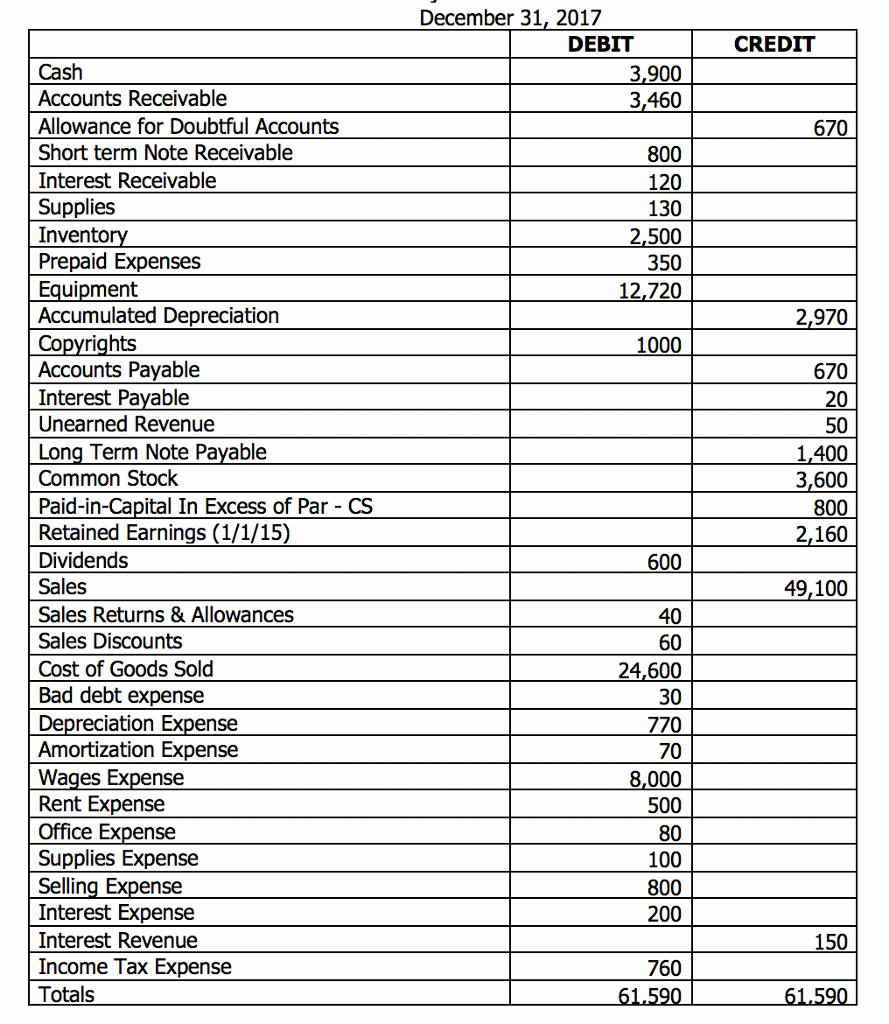
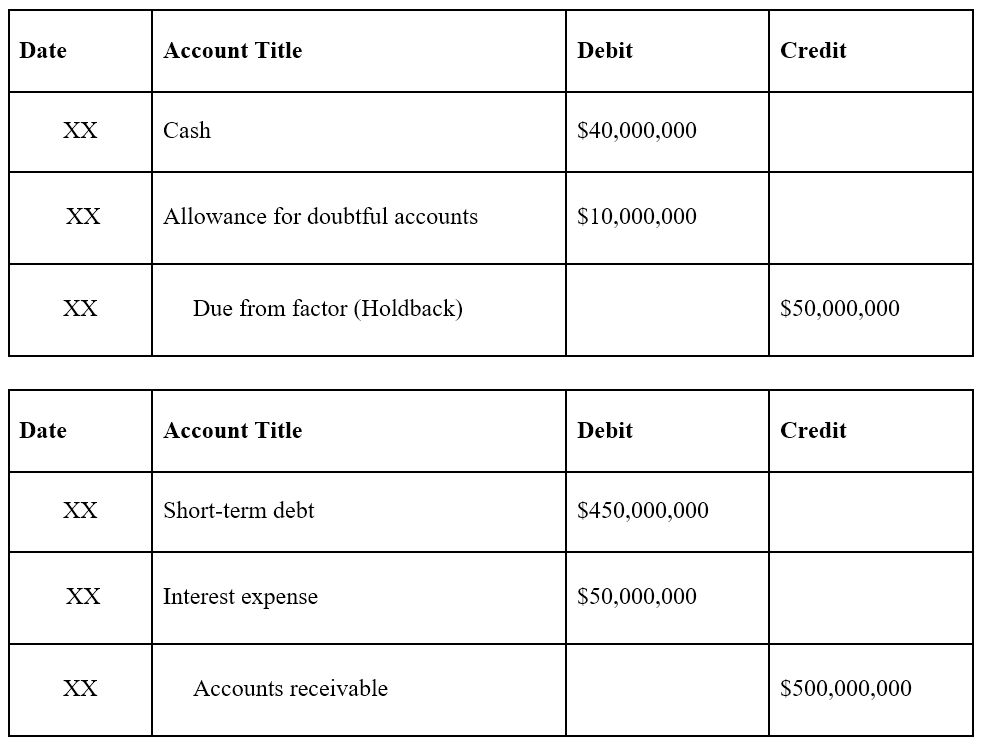
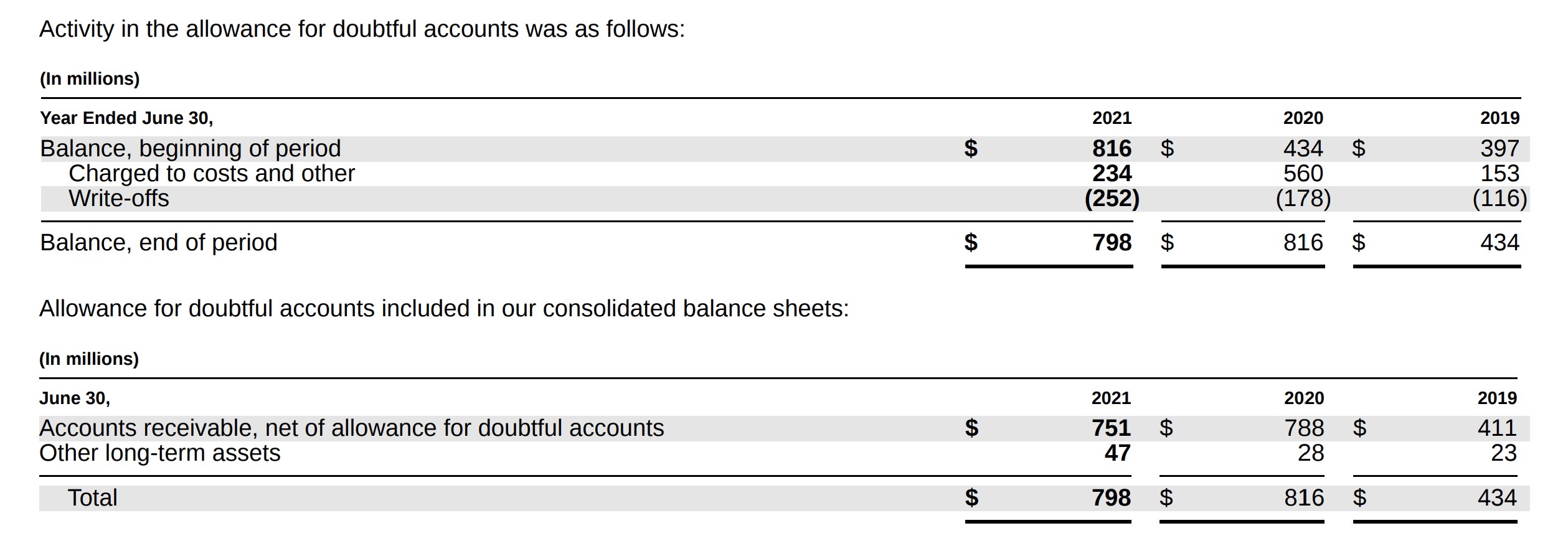
Allowance For Doubtful Accounts On Balance Sheet - This deduction is classified as a. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers owe that will never come in. What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable. The doubtful account in balance, which records. Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those.
What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The doubtful account in balance, which records. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those. The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers owe that will never come in. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. This deduction is classified as a.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers owe that will never come in. Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable. This deduction is classified as a. The doubtful account in balance, which records.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Definition and Examples Bookstime
The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100.
Accounting Unit 5 Part 3 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable..
allowancefordoubtfulaccounts8
The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable. What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Balance Sheet Example YouTube
The doubtful account in balance, which records. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about.
How to Account for Doubtful Debts 11 Steps (with Pictures)
The doubtful account in balance, which records. This deduction is classified as a. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The purpose of the allowance.
Accounts Receivable Journal Entry Example Accountinguide
The doubtful account in balance, which records. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers owe that will never come in. This deduction is classified as a. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. What is an allowance for doubtful.
Classified Balance Sheet Allowance For Doubtful Accounts
The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The doubtful account in balance, which records. This deduction is classified as a. The $1,000,000 will be reported.
Bad Debt Expense and Allowance for Doubtful Account Accountinguide
Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. The doubtful account in balance, which records. This deduction is classified.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Personal Accounting
The doubtful account in balance, which records. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. This deduction is classified as a. Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of.
Allowance for Doubtful Debt Double Entry
Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a company's educated guess about how much customers owe that will never come in. What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how.
Accounts Receivable Present In The Balance Sheet Is The Net Amount, Which Remains After Deducting The Allowance For The Doubtful Account.
What is an allowance for doubtful accounts? The doubtful account in balance, which records. This deduction is classified as a. The $1,000,000 will be reported on the balance sheet as accounts receivable.
The Allowance For Doubtful Accounts Is A Company's Educated Guess About How Much Customers Owe That Will Never Come In.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. The purpose of the allowance for doubtful accounts is to estimate how many customers out of the 100 will not pay. Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those.