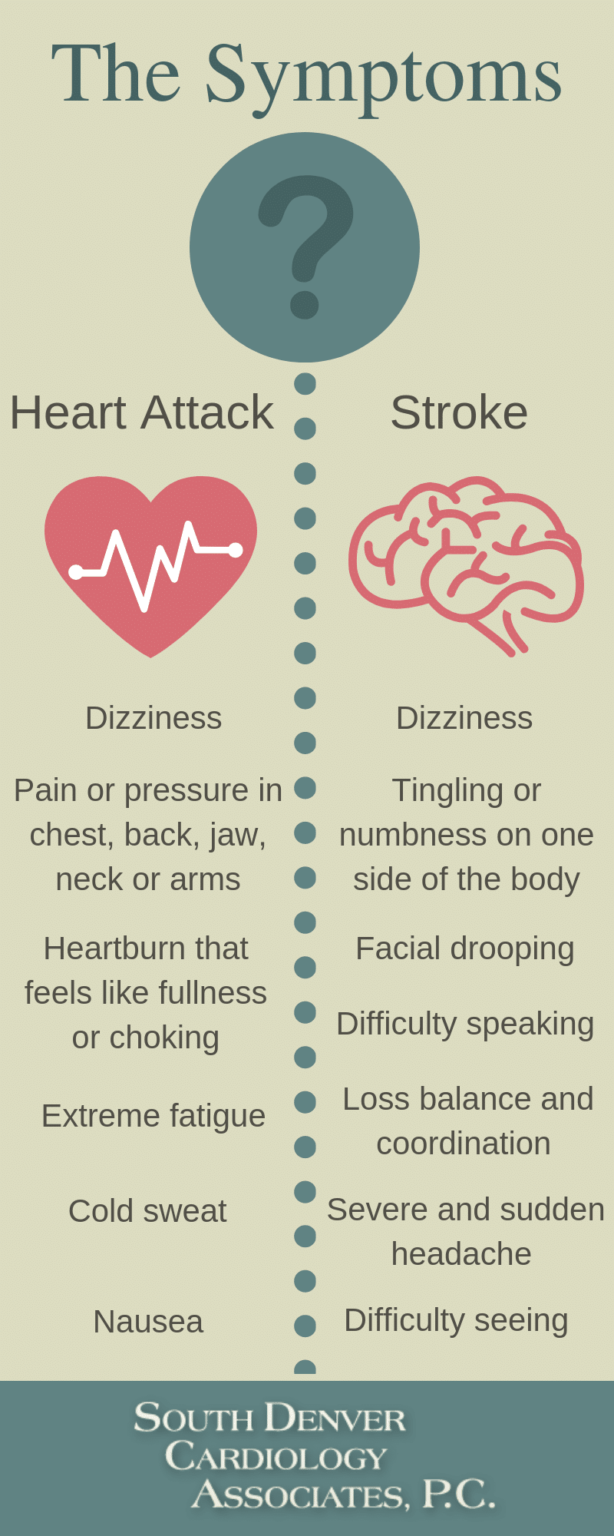
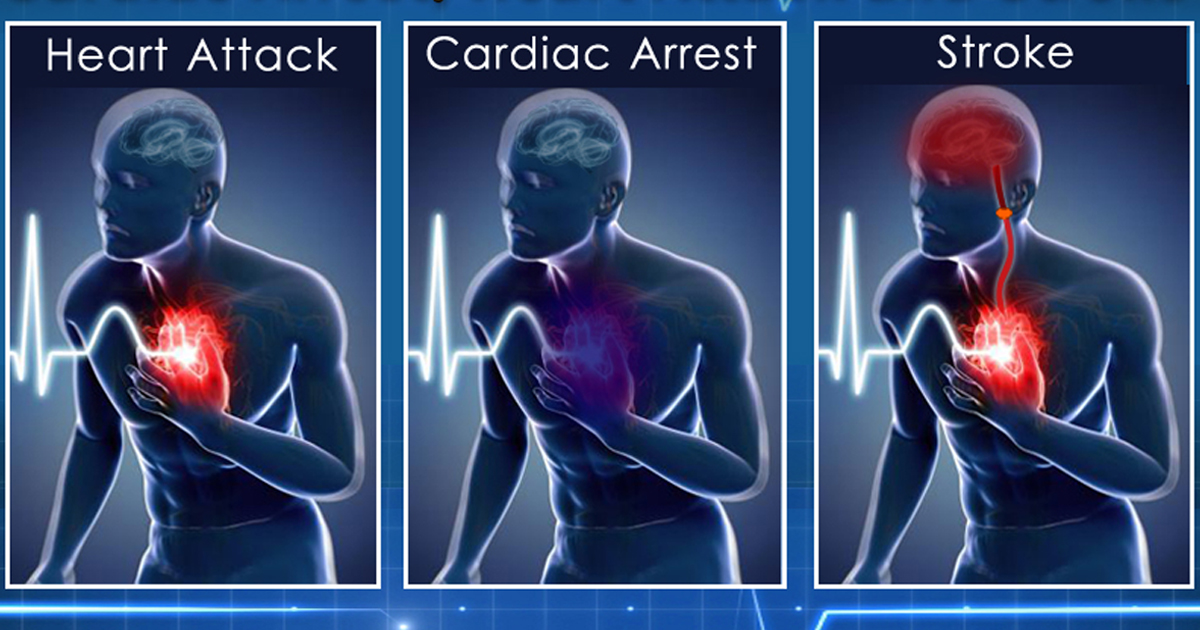
Can Cardiac Arrest Cause Stroke - Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. This pathological connection is supported by. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest.
This pathological connection is supported by. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood.
Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. This pathological connection is supported by. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest.
Cardiac Arrest And Strokes Understanding The Link MedShun
Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. This pathological connection is supported by. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke.
Understanding Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack, and Stroke
While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac.
Heart Attack Vs. Stroke What’s the Difference? (Infographic) South
Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. This pathological connection is supported by. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of.
Cardiovascular Diseases Among Elderly In Singapore Understand And
This pathological connection is supported by. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing.
Photo Cardiac Arrest vs. Heart Attack American Heart Association
Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. This pathological connection is supported by. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke.
"Do you know the difference between a cardiac arrest and a stroke
This pathological connection is supported by. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated.
Learn the Key Differences Among, Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack and
Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. This pathological connection is supported by. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after.
Know the difference between a heart attack, a cardiac arrest and a
This pathological connection is supported by. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical..
Stroke vs heart attack PatientEducationMD
Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest had a high incidence and was associated with poor outcomes after ischemic stroke, including multiple medical. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. This.
Understanding Heart Attack, Cardiac Arrest and Stroke Cardiac arrest
This pathological connection is supported by. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs.
Cardiac Arrest Had A High Incidence And Was Associated With Poor Outcomes After Ischemic Stroke, Including Multiple Medical.
Not only can cardiac arrest cause a stroke, but a stroke can also trigger cardiac arrest. Neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest cardiac arrest may be thought of as causing both metabolic and structural damage to the. While stroke is caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood. This pathological connection is supported by.