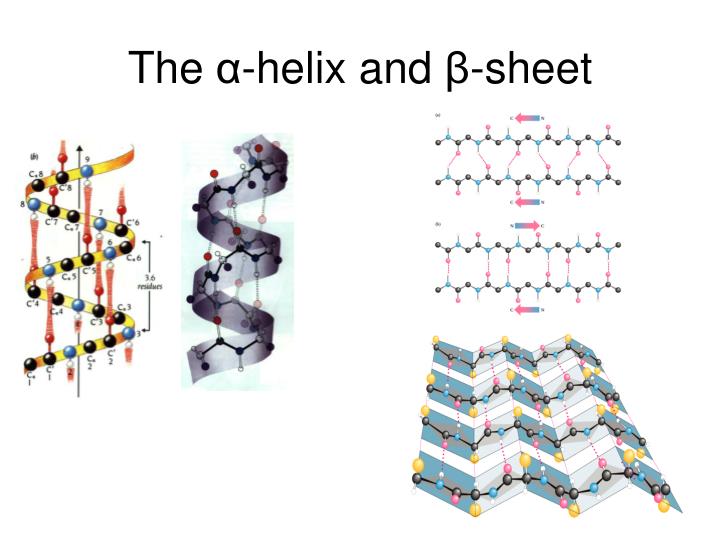
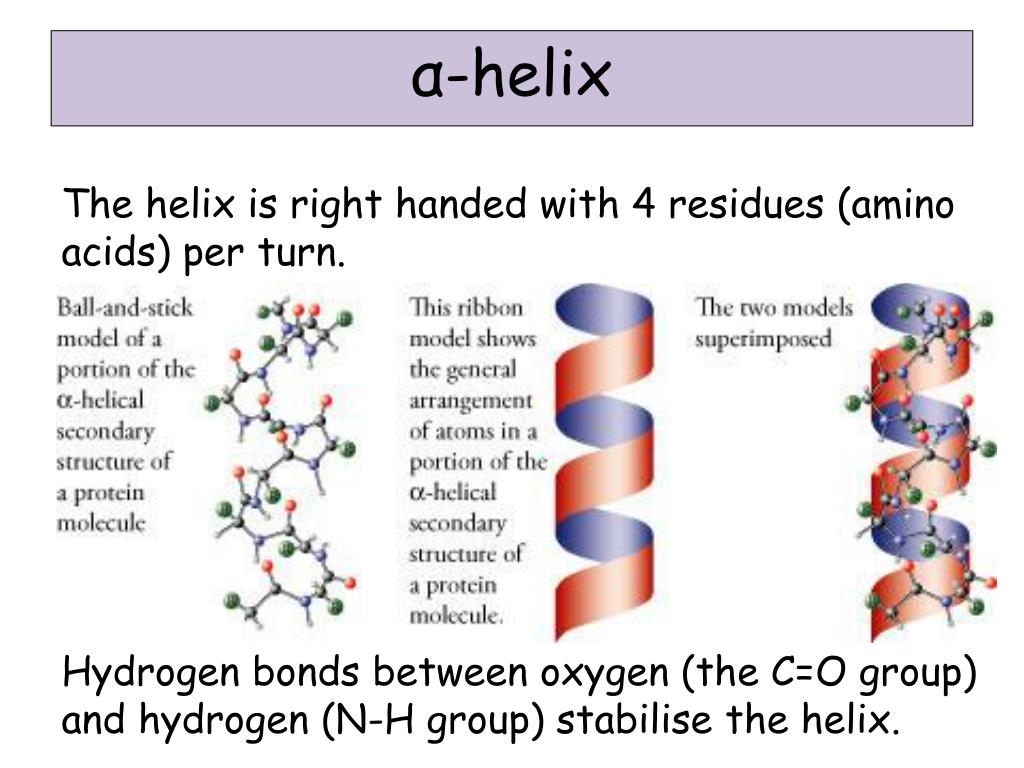
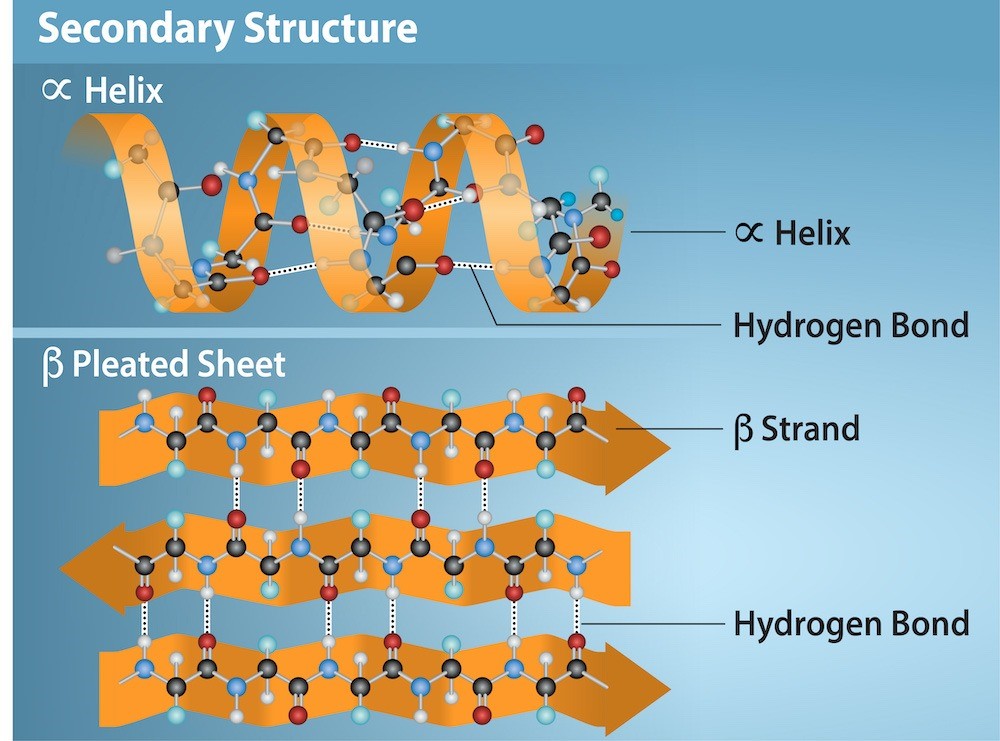
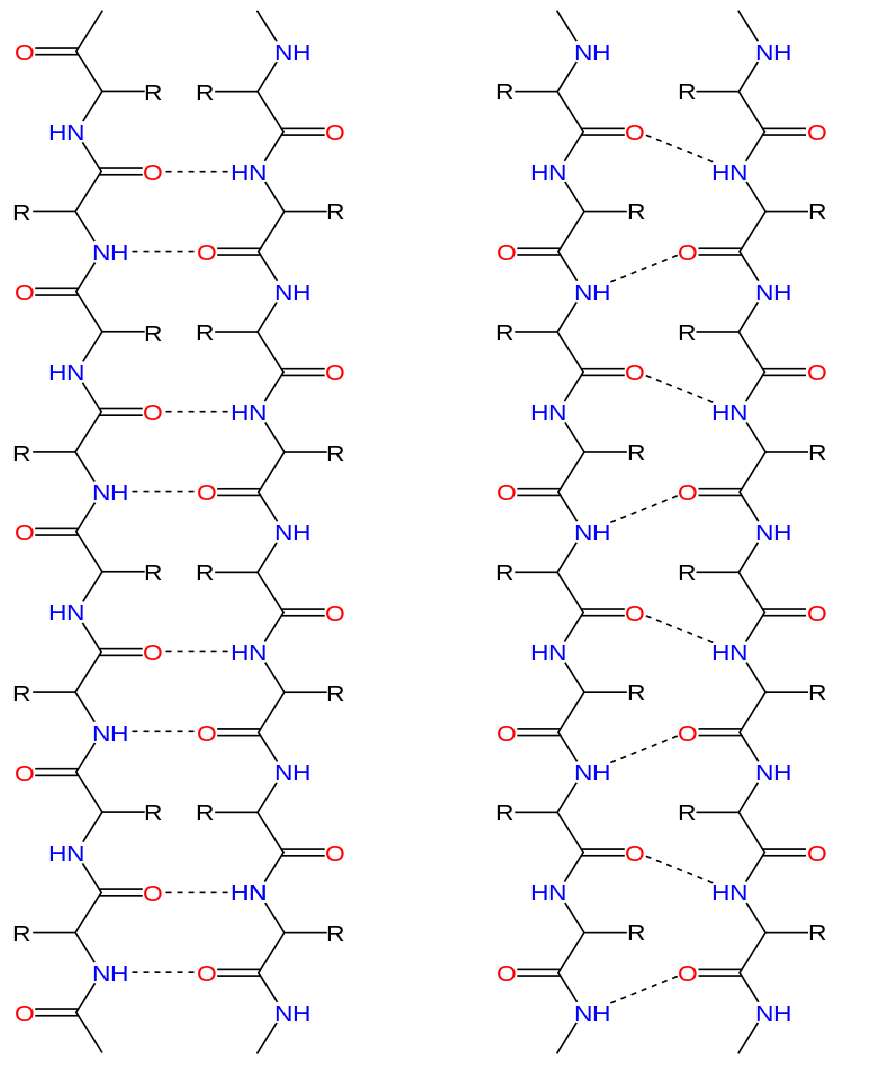
Difference Between Alpha Helix And Beta Sheet - Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser.
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser.
Difference between Alpha Helix and Beta Helix
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or.
PPT Spectroscopy of Proteins PowerPoint Presentation ID6052251
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated.
PPT Lesson 5 Proteins Levels of Protein Structure PowerPoint
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major.
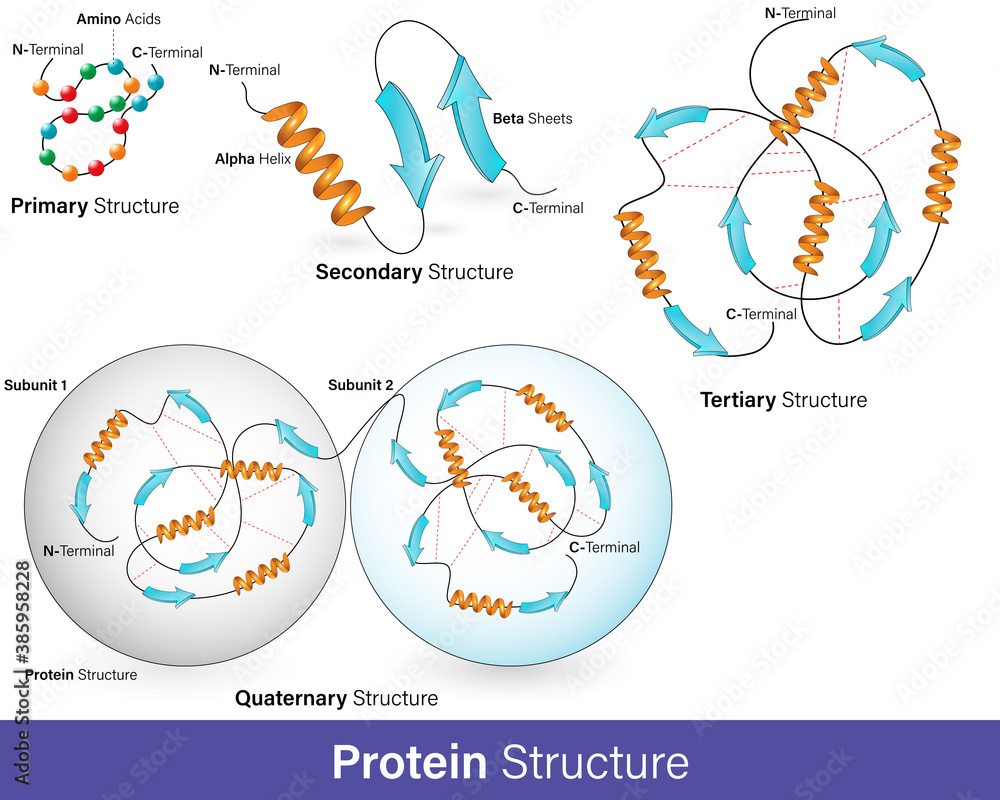
vector illustration of Hierarchy of protein structure. alpha helix and
In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major.
Chapter 21 Protein Structure and Function Introductory Biology I
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated.
2 The two most common types of protein secondary structure, αhelices
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated.
Difference between Alpha Helix and Beta Sheets YouTube
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated.
College. Science. Life Essential Cell Biology 3rd Ch 4 Protein
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). In this definition of alpha helix, sheets are characterised through their tight pleats, while in beta pleated sheets, they have looser. While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or.
In This Definition Of Alpha Helix, Sheets Are Characterised Through Their Tight Pleats, While In Beta Pleated Sheets, They Have Looser.
While both structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonding, the alpha helix is more flexible and can be found in the interior or on the surface of. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\).