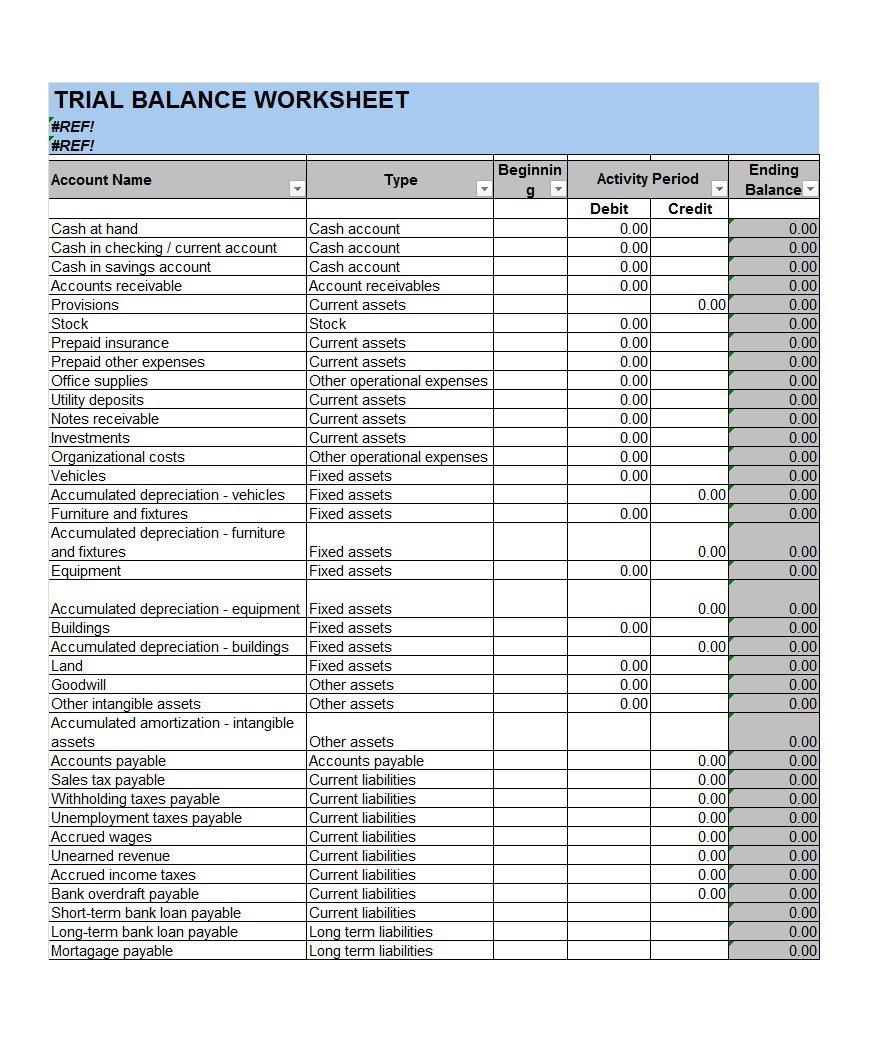
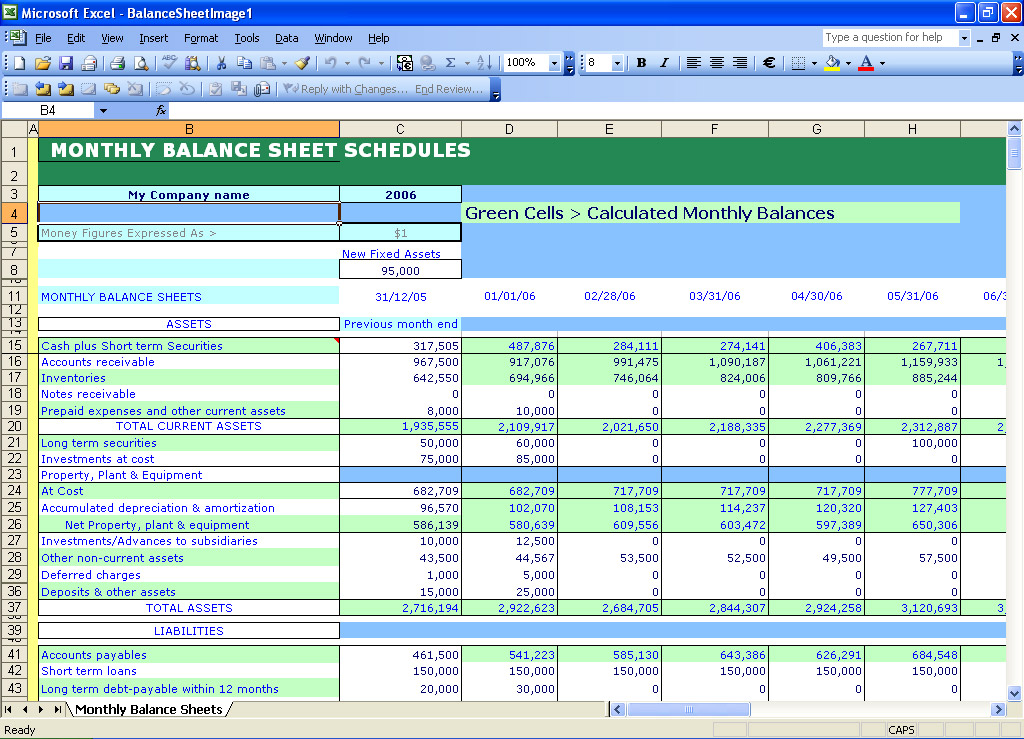
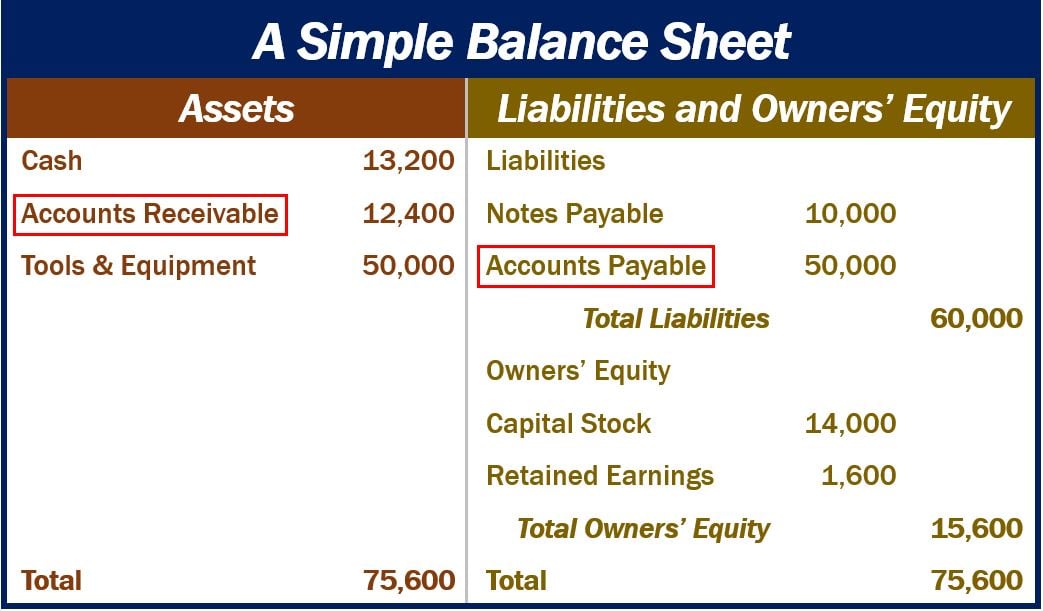
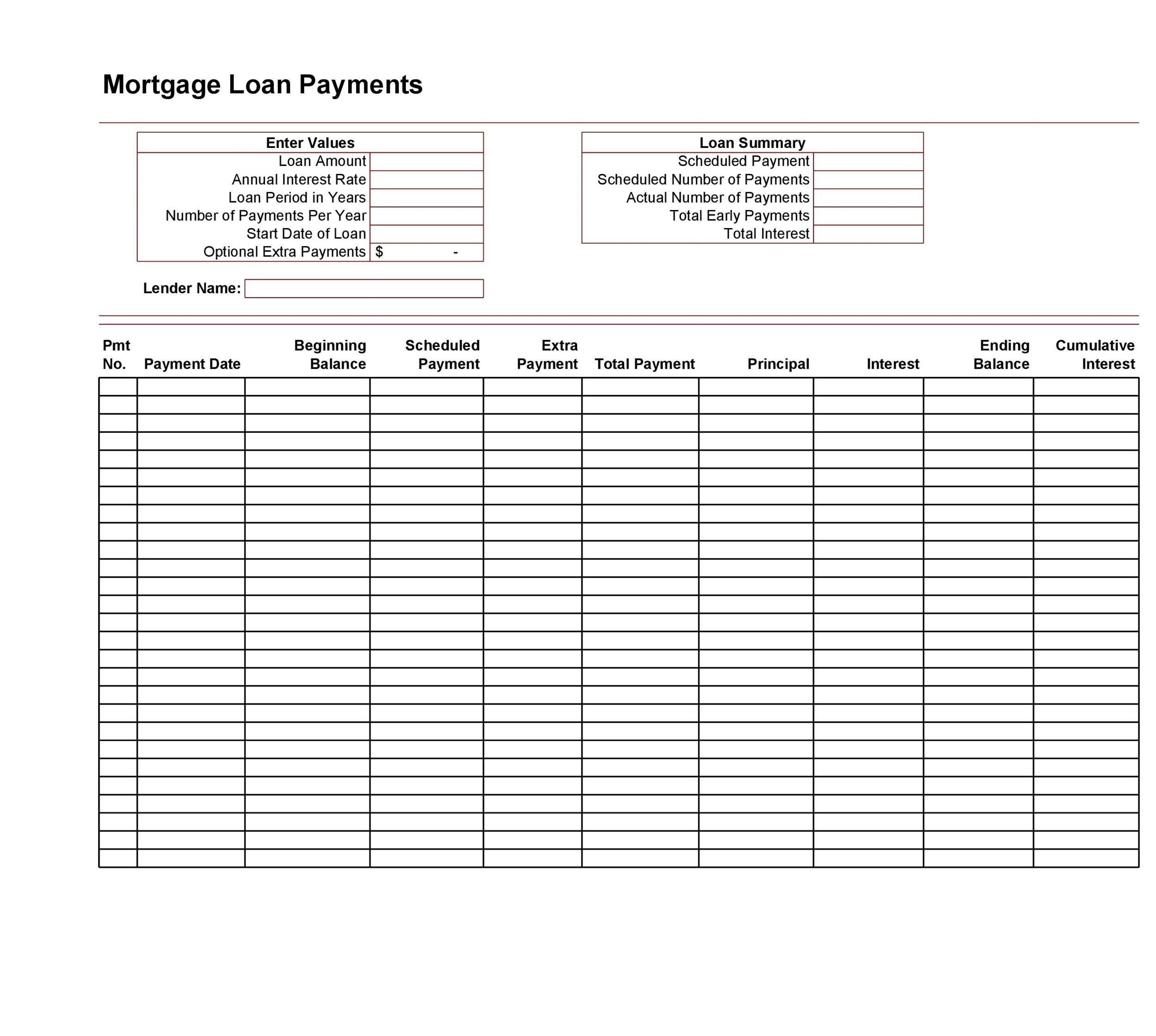
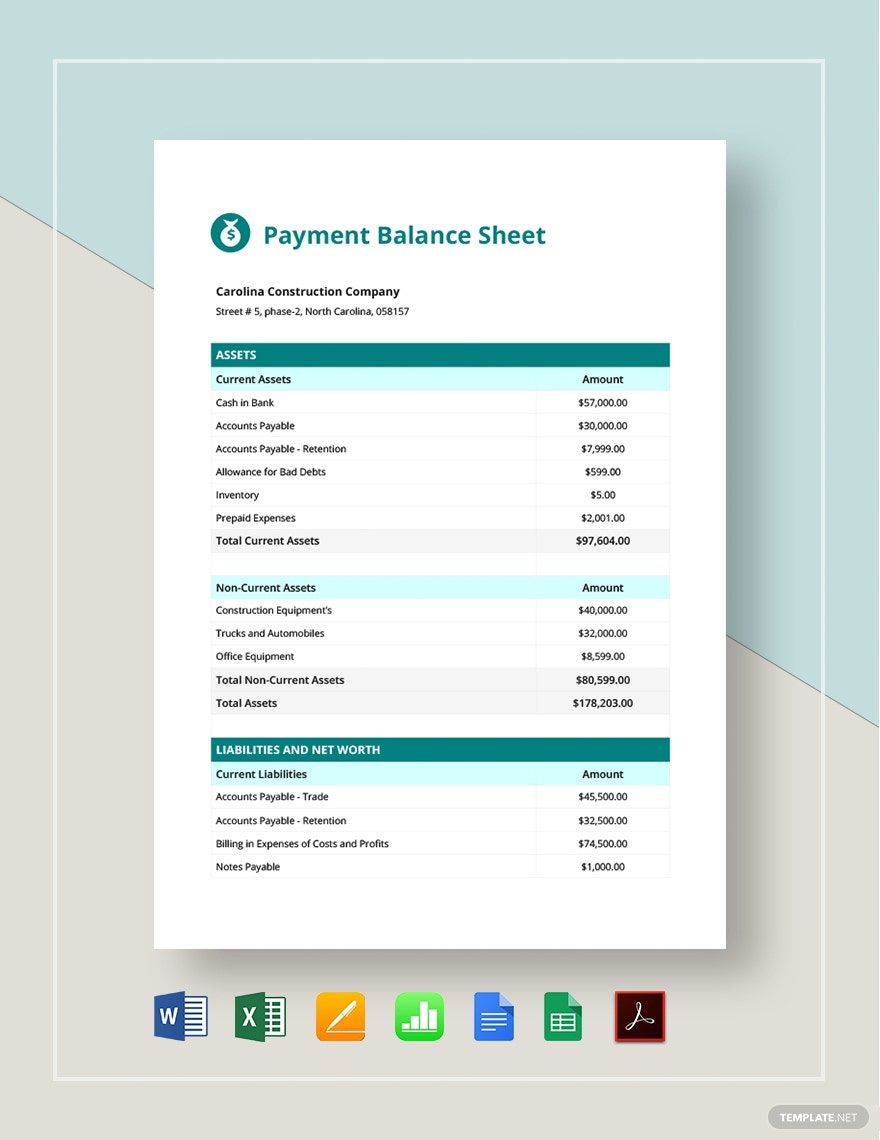
Interest Payment Balance Sheet - When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or patterns that.
Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or patterns that. When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28.
Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or patterns that. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance.
EXCEL of Monthly Balance Sheet.xlsx WPS Free Templates
You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies.
Account Balance Spreadsheet Template with 38 Free Balance Sheet
Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or.
Noncontrolling Interests The Full Consolidation Accounting Tutorial
Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is.
balance sheet template excel mac —
When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. You would include the.
Business Interests Understanding Receivables and Inventory
Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment.
excel ledger template with debits and credits Balance sheet template
Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. When you make that loan payment, you.
28 Tables to Calculate Loan Amortization Schedule (Excel) ᐅ TemplateLab
When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. Generate regular reports on.
Payment Log Sheet Template in Excel, Google Sheets Download
Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is.
How To Calculate Credit Card Interest Excel
Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or patterns that. Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so.
Biweekly mortgage calculator with extra payments [Free Excel Template
When you make that loan payment, you pay interest up to december 28. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies.
When You Make That Loan Payment, You Pay Interest Up To December 28.
Interest expense is an expense, and so appears on the income statement, while interest payable is a liability, and so appears on. You would include the interest for december 29, 30, and. Generate regular reports on loan balances, payment status, and overdue accounts, and review them for anomalies or patterns that. Add “interest payable,” which is the amount of interest the company owes (not yet paid), under “current liabilities” on the balance.