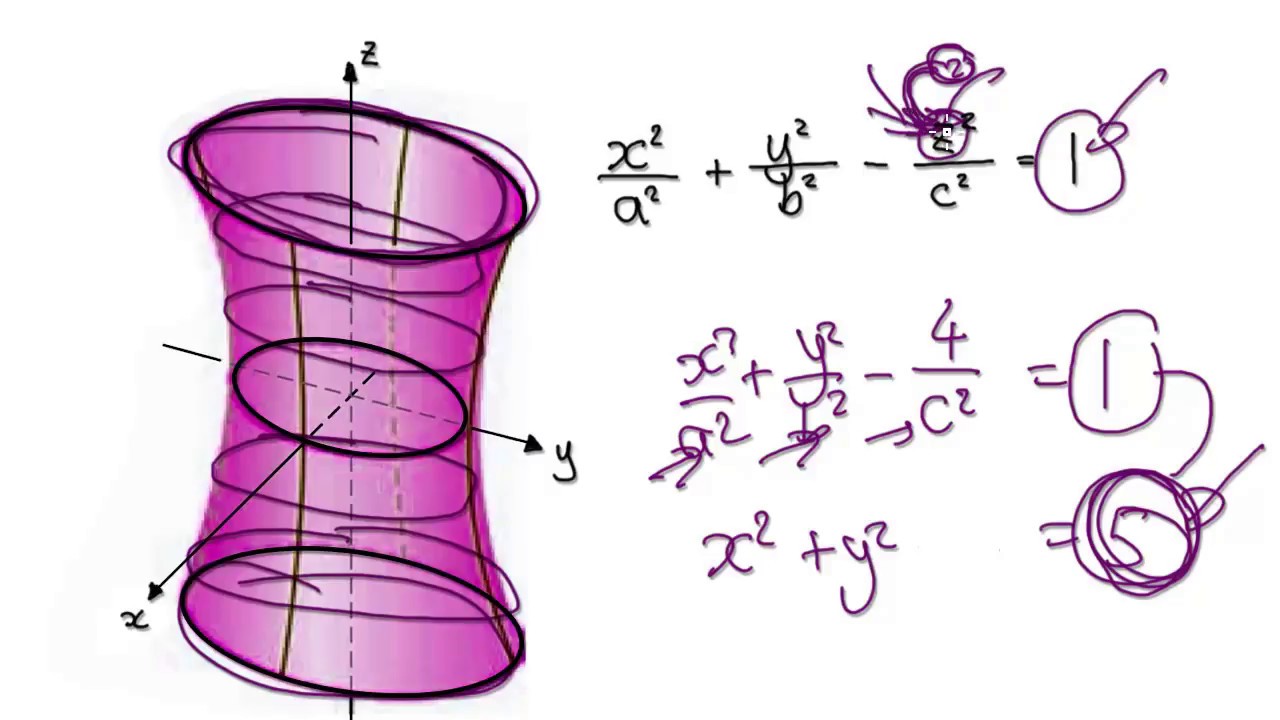
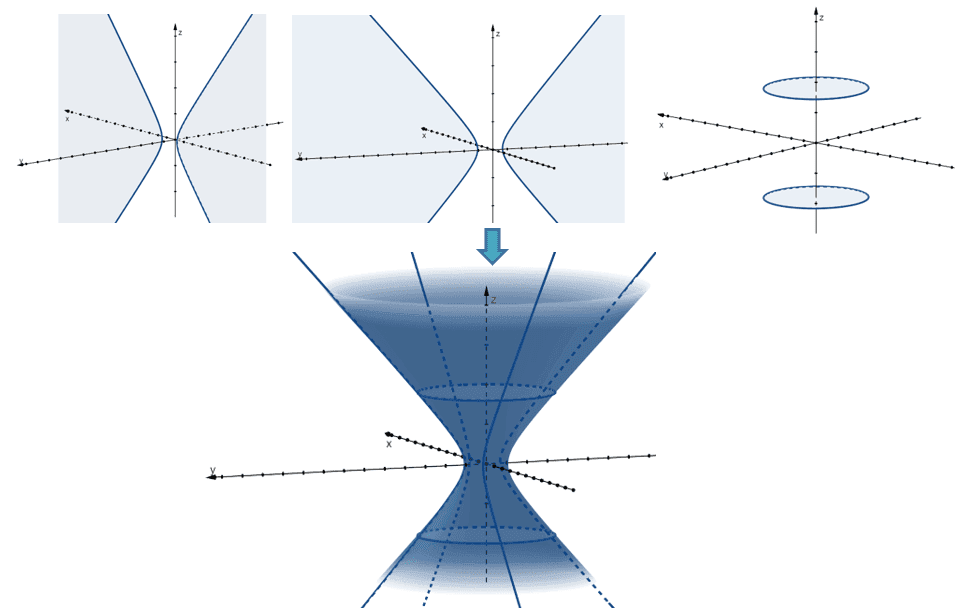
One Sheet Hyperboloid Equation - Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet.
The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\).
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The diameter at the base is 280 m.
Video 2962 Calculus 3 Quadric Surfaces Hyperboloid of one sheet
A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. Here is the equation.
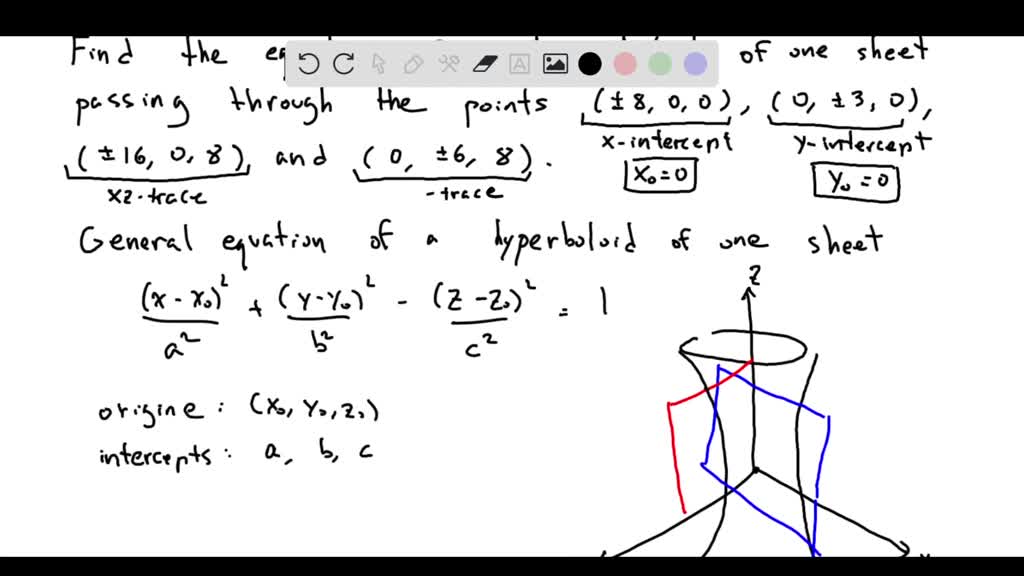
SOLVED Find the equation of the hyperboloid of one sheet passing
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an.
Graphing a Hyperboloid of One Sheet in 3D YouTube
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The horizontal.
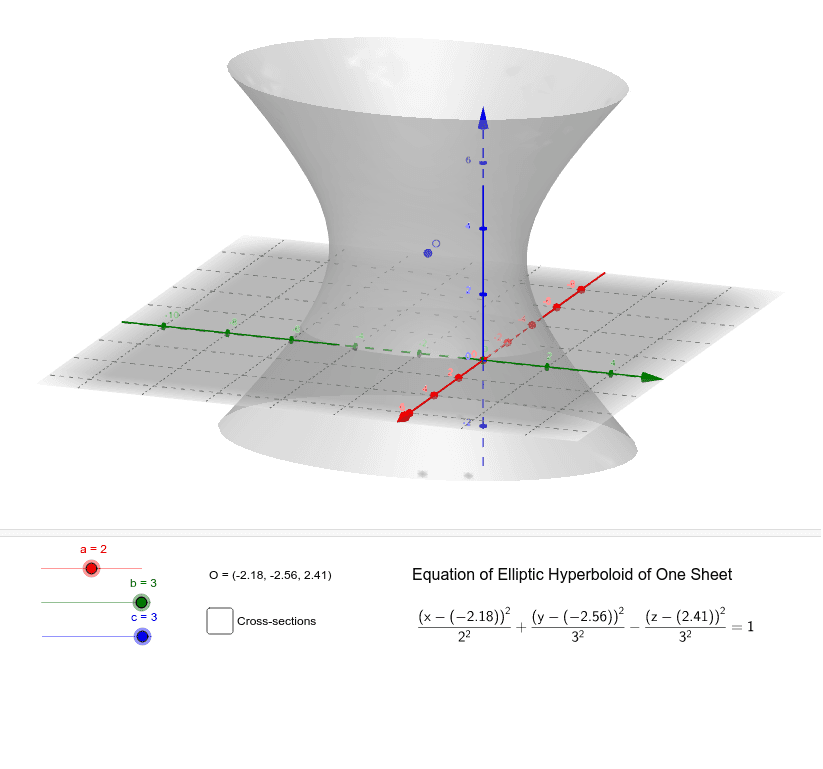
Elliptic Hyperboloid of One Sheet GeoGebra
The diameter at the base is 280 m. Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape.
Chapter 12Section6 Quadric Surfaces ppt video online download
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an.
Hyperboloid of One Sheet
The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The horizontal.
QuadraticSurfaces
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an.
Quadric surfaces Definition, Types, and Examples
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The horizontal.
Quadric Surfaces (Identified and Explained w/ Examples!)
The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an.
Quadric Surface The Hyperboloid of One Sheet Vector Calculus YouTube
Here is the equation of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\). The diameter.
Here Is The Equation Of A Hyperboloid Of One Sheet.
The horizontal cross sections are ellipses — circles,. A cooling tower for a nuclear reactor is to be constructed in the shape of a hyperboloid of one sheet. The diameter at the base is 280 m. A hyperboloid of one sheet is any surface that can be described with an equation of the form \( \dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}−\dfrac{z^2}{c^2}=1\).